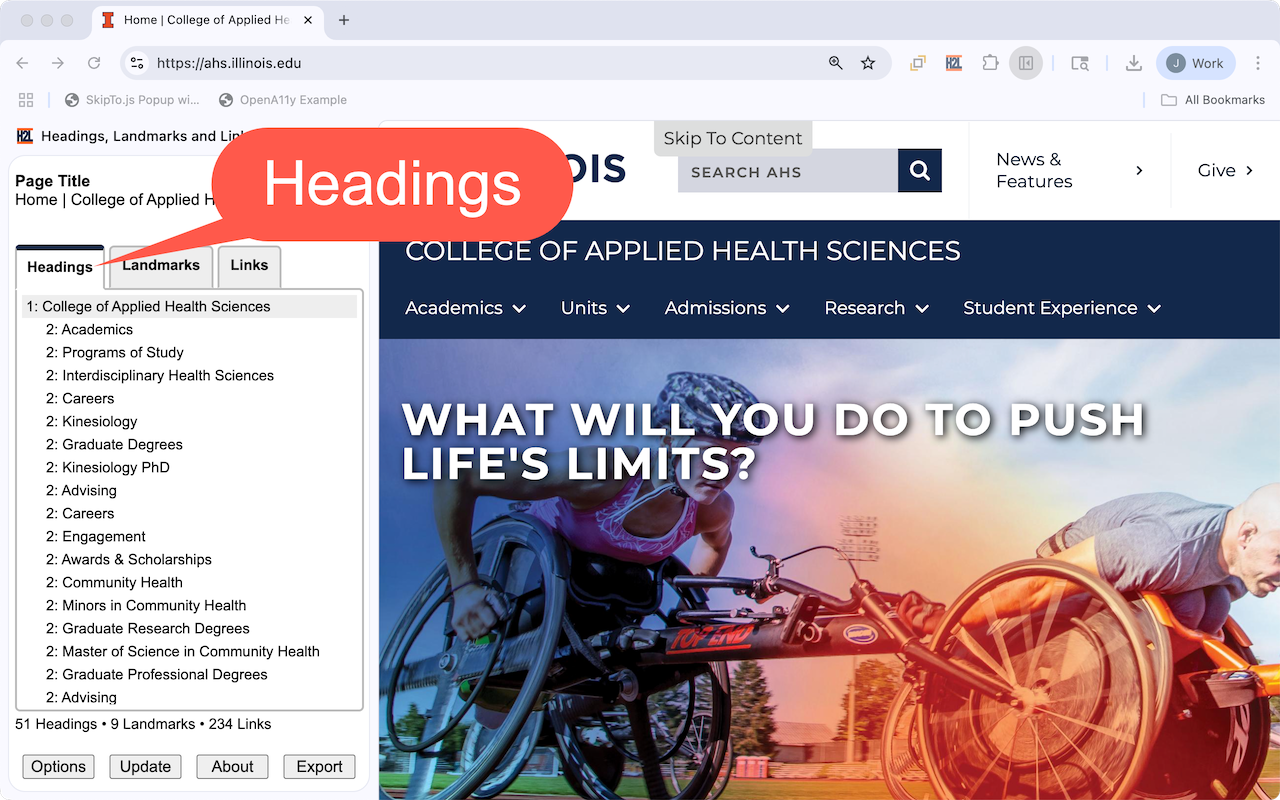
Headings Tab
Feature
-
The first tab provides a tree view of the heading (e.d. the
h1,h2,h3,h4h5andh6elements) structure of a web page. - Each tree item provides the heading level and the accessible name used by screen readers.
- The tree items are indented based on their heading level.
- Headings level 3 and higher are initially hidden in the tree.
- Note: Some authors add hidden or off-screen headings that are intended only for screen reader users and cannot be seen in the graphical rendering. These headings are not included in the list of headings by default. This mimics the behavior of many screen readers to reduce the number of headings users have to navigate. This feature can be disabled in options.
Accessibility Considerations
- Descriptive: Verify headings accurately reflect the content they introduce. For example, a heading "Ingredients" should be followed by a list of ingredients, not instructions on how to prepare them.
-
Logical Hierarchy: Verify headings are used in a hierarchical order, typically starting with
h1for the main page title, followed byh2for main sections,h3for subsections, and so on. Avoid skipping heading levels (e.g., going directly fromh1toh3). - Unique Headings: Verify headings in the same sub-section are unique. This prevents confusion for users, especially those using screen readers, who rely on headings for navigation.
- Concise and Clear: Verify headings are relatively short and to the point, avoiding overly long or complex phrasing.
- Related WCAG Requirements:
- 1.3.1 Info and Relationships: Information, structure, and relationships conveyed through presentation can be programmatically determined or are available in text. (Level A)
- 2.4.1 Bypass Blocks: A mechanism is available to bypass blocks of content that are repeated on multiple Web pages. (Level A)
- 2.4.6 Headings and Labels: Headings and labels describe topic or purpose. (Level AA)
- 2.4.10 Section Headings: Section headings are used to organize the content. (Level AAA)
- W3C WAI Tutorials on Headings